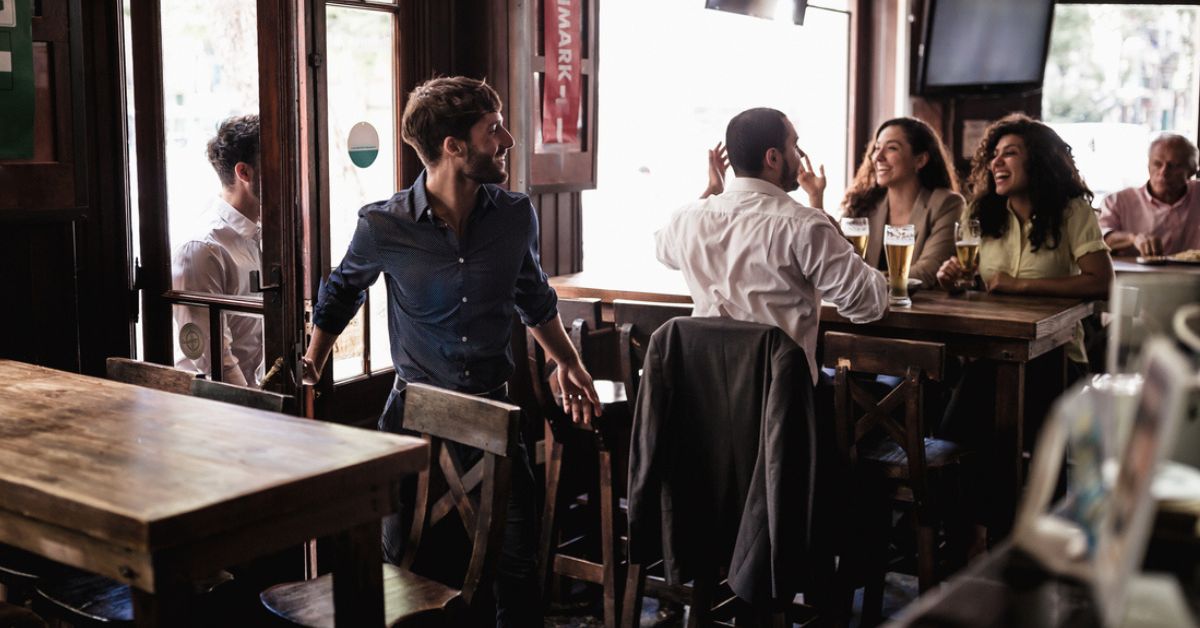
Cravings are a common yet complex phenomenon experienced by individuals while undergoing addiction treatment. They can be described as intense desires or urges for a particular substance or behavior that one tries to abstain from, often seen in individuals with substance use disorder. These cravings have both physiological roots, such as changes in brain chemistry due to past substance use, and psychological components, including emotional states and thought patterns.
Understanding the dual nature of cravings is crucial in addiction recovery, as it allows individuals to address both the body’s and the mind’s calls for a substance, thereby improving their chances of maintaining sobriety. This article explains everything you need to know about coping with cravings while recovering from substance abuse.
Definition and Nature of Addiction Cravings
Cravings manifest as powerful and persistent urges that can be challenging to resist. They are often triggered by specific cues or situations, which can vary greatly from person to person.
Recognizing these triggers is a vital step in managing cravings, as it enables individuals to develop strategies to either avoid or confront these cues with greater resilience.
What Causes Cravings in Addiction Recovery?
Cravings in addiction recovery are a complex phenomenon that can be triggered by various factors. Understanding the causes of cravings is essential for developing effective coping strategies.
Some common causes of cravings in addiction recovery include:
- Withdrawal Symptoms: When an individual stops using a substance, their body may experience withdrawal symptoms, which can trigger cravings. These symptoms are a normal and expected part of the recovery process, but they can be challenging to manage without proper support.
- Stress and Anxiety: Stress and anxiety are significant triggers for cravings. Individuals may turn to substances as a way to cope with negative emotions, seeking the temporary relief that past substance use provided. Learning healthy stress management techniques is crucial in these situations.
- Environmental Cues: Environmental cues such as people, places, or things associated with past substance use can trigger cravings. For example, visiting a location where one used to use substances or encountering friends who still engage in substance use can prompt strong urges.
- Internal Triggers: Internal triggers, such as emotional lows, positive memories of past substance use, or feelings of boredom, can also trigger cravings. These internal states can be powerful reminders of the temporary comfort substances once provided, making it essential to develop new, healthy ways to address these feelings.
- Brain Changes: Brain changes that occur during active addiction can contribute to cravings. The brain associates substance use with positive feelings, creating a powerful drive to seek out those substances again. Understanding these changes can help individuals recognize that cravings are a normal part of the recovery journey and not a sign of failure.
How to Identify Personal Triggers
Identifying personal triggers is a crucial step in managing cravings in addiction recovery.
Here are some steps to help you identify your personal triggers:
- Keep a Journal: Keeping a journal can help you track your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, making it easier to identify patterns and triggers. Write down when cravings occur, what you were doing, and how you were feeling at the time. Over time, you may notice specific situations or emotions that consistently trigger cravings.
- Reflect on Past Experiences: Reflecting on past experiences can help you identify situations, people, or emotions that triggered substance use. Think about the times when you felt the strongest urges to use substances and what was happening in your life at those moments.
- Seek Support: Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can provide additional help and guidance in identifying personal triggers. Sometimes, an outside perspective can offer insights that you might not see on your own. Support groups can also be a valuable resource for sharing experiences and learning from others.
- Practice Self-Awareness: Practicing self-awareness can help you become more aware of your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, making it easier to identify triggers. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can enhance your ability to stay present and recognize when a craving is starting to build.
Strategies for Managing Cravings
Effective addiction treatment programs incorporate various strategies to help individuals manage cravings and maintain sobriety.
With this in mind, here’s how to navigate cravings in recovery:
1. Mindfulness and Coping Techniques
Mindfulness is a powerful tool in the arsenal against cravings. It involves staying present and fully engaged in the current moment without judgment. This practice can help individuals in recovery observe their cravings without acting on them. Techniques such as meditation and deep breathing exercises can anchor someone in the present and provide a sense of calm that counteracts the urgency of cravings. Mindfulness encourages a reflective rather than reactive approach to cravings, allowing individuals to recognize these urges’ impermanent nature and respond with intention rather than impulse.
Developing a set of coping techniques is essential for managing cravings. These can include engaging in a hobby, talking to a supportive friend or family member, or practicing relaxation techniques. The key is to have a variety of strategies to turn to, as what works in one situation may not be as effective in another. It’s also important for these techniques to be readily accessible so individuals can employ them quickly when cravings arise.
2. Creating a Supportive Environment
A supportive environment is a cornerstone of successful recovery. This involves changing one’s living space, routine, and social interactions to minimize exposure to triggers and foster a recovery-friendly atmosphere. It might mean removing substances from the home, avoiding certain social gatherings, or creating new, healthy rituals that reinforce sobriety. The goal is to construct an environment that reduces the likelihood of encountering triggers and promotes well-being and resilience against cravings.
Friends and family play a critical role in shaping a supportive environment. It’s beneficial for individuals in recovery to communicate their needs and boundaries to their loved ones, ensuring that their support network understands how to assist them best. This might involve establishing new ways to socialize that do not involve substance use or participating in recovery groups together.
3. Nutritional Wellness
Nutrition often plays an underappreciated role in the recovery process. A balanced diet can profoundly impact managing cravings, as proper nutrition helps stabilize mood, improve energy levels, and support overall physical health. Consuming a diet rich in whole foods, vitamins, and minerals can aid in repairing the body and brain from the damage of substance abuse. Additionally, certain foods can help balance neurotransmitter levels, which may reduce the intensity and frequency of cravings.
Cravings can sometimes be misinterpreted signals from the body, such as hunger or nutritional deficiencies. By paying attention to regular meal patterns and nutritional intake, individuals can better discern between true cravings for substances and the body’s need for nourishment. Staying hydrated and maintaining a diet that includes a variety of nutrients can also help reduce the temptation to turn to substances for comfort or stimulation. Nutrition is not just about physical health; it’s an integral part of a holistic approach to recovery that acknowledges the interplay between body and mind.
4. Exercise as a Tool for Craving Management
Physical activity is another valuable tool for those working to manage cravings. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters, and can help alleviate some of the emotional triggers for cravings, such as stress or anxiety. Regular exercise also promotes better sleep, increases energy levels, and can improve self-esteem, all of which benefit individuals in recovery. Whether it’s a daily walk, a yoga session, or a more intense workout, incorporating physical activity into one’s routine can be a healthy distraction and a positive outlet for managing cravings.
Exercise helps with immediate craving management and contributes to long-term recovery success. Establishing a routine that includes physical activity can help create structure in one’s life, which is often needed after the chaos of addiction. It also provides an opportunity to set and achieve goals, which can empower individuals in recovery. By understanding the psychological and physiological benefits of exercise, those in recovery can use it as a proactive strategy to strengthen their resolve and maintain their commitment to sobriety.
5. Cognitive-Behavioral Strategies
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective treatment modality for addiction recovery. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to substance abuse. By applying CBT techniques, individuals can learn to recognize the thought processes that lead to cravings and develop healthier responses. Strategies such as challenging irrational beliefs, practicing problem-solving skills, and engaging in behavioral experiments can empower those in recovery to take control of their cravings and reduce their impact.
One of the key benefits of CBT is its focus on practical skills that can be applied in real-world situations. For instance, individuals can learn to anticipate potential triggers and plan accordingly, reducing the likelihood of encountering situations that might provoke cravings. Through role-playing and other CBT exercises, individuals can also build confidence in their ability to resist cravings and remain sober.
6. Emotional Regulation and Recovery
Emotional regulation is a critical skill for managing cravings and sustaining recovery. It involves understanding and managing one’s emotional responses, rather than being controlled by them. Developing emotional regulation can help individuals recognize the emotional underpinnings of their cravings and address them in a healthy manner. Techniques such as journaling, expressive arts, and therapy can provide outlets for processing emotions and reducing the intensity of cravings that are tied to emotional states.
By improving emotional regulation, individuals can better handle stress, anxiety, and other emotions that might otherwise lead to relapse. This skill set enables them to face life’s ups and downs with greater resilience and to maintain their sobriety even in the face of emotional challenges. Emotional regulation is a cornerstone of a sustainable recovery, as it equips individuals with the ability to manage their internal world and the external triggers they encounter.
7. Building a Relapse Prevention Plan
Creating a personalized relapse prevention plan is a proactive step toward maintaining long-term recovery. This plan should address individual triggers, outline effective coping strategies, and include a support system that can be called upon when needed. A relapse prevention plan is not static; it should be reviewed and adjusted regularly to reflect the person’s growth and changes in their recovery journey.
A comprehensive relapse prevention plan also includes strategies for dealing with high-risk situations and an emergency plan for what to do during a lapse. Individuals must recognize that a lapse doesn’t have to lead to a full-blown relapse; with the right plan, they can get back on track quickly. The plan should also encourage ongoing engagement with recovery activities, such as attending support groups or therapy sessions, to reinforce the commitment to sobriety.
8. Celebrating Milestones and Sustaining Motivation
Celebrating milestones is an essential part of the recovery process. Acknowledging the hard work and dedication it takes to reach each new stage of sobriety can provide a sense of accomplishment and reinforce the value of staying sober. Whether it’s marking one month or one year of sobriety, these milestones are opportunities to reflect on progress and to thank those who have supported the journey. Celebrations can be personal and simple, like taking time for self-care or sharing with loved ones meaningfully.
Sustaining motivation over the long term can be challenging, but it’s crucial for ongoing recovery. Setting new goals, exploring new interests, and continuing to grow personally and professionally can all contribute to a sense of purpose and direction. Staying connected with the recovery community and helping others on their path can also provide a powerful motivation to maintain one’s own sobriety.
Understanding the Cycle of Addiction
Understanding the cycle of addiction is essential for developing effective coping strategies. The cycle of addiction includes:
- Trigger: A trigger is a stimulus that prompts a craving. This could be an external trigger, like seeing a place where you used to use substances, or an internal trigger, such as feeling stressed or anxious.
- Craving: A craving is a strong desire or urge to use a substance. Cravings can be intense and persistent, making it challenging to resist the urge to use. Recognizing that cravings are a normal and expected part of the recovery process can help you manage them more effectively.
- Use: Using a substance can lead to feelings of pleasure and relaxation, but it can also lead to negative consequences. The temporary relief that substances provide can reinforce the cycle, making it harder to break free.
- Guilt and Shame: Feeling guilty or ashamed about substance use can lead to feelings of low self-esteem and self-worth. These negative emotions can, in turn, become triggers themselves, perpetuating the cycle of addiction.
Recognizing the stages of the cycle allows you to intervene early, using the tools and techniques you’ve learned to break the cycle and maintain your sobriety.
Navigate Cravings in Recovery with The Lakes Treatment Center
At The Lakes Treatment Center in Copperopolis, CA, we understand how to help you manage cravings and triggers during recovery. Our comprehensive addiction medicine services are designed to support you every step of the way, from personalized therapies to nutritional guidance and wellness programs.
If you or a loved one is seeking a supportive environment to overcome addiction, we invite you to contact us. Contact us today and take the first step towards a future free from addiction. We can build a foundation for long-term success and a healthier, happier life.